VLSI Symposium tipsheet offers a preview of two image sensor papers:
A 3D stacked CMOS Image Sensor with Global-shutter mode and high speed capturing mode:
The paper by Toru Kondo et al. from Olympus Corp. will describe a 16MP 3D stacked CMOS image sensor with pixel level interconnections using 4 million micro bumps. The two semiconductor substrates are bonded by a 7.6um pitch micro-bump array, and the storage node array is comprised on the bottom substrate to improve parasitic light sensitivity (PLS). Both a 16Mpixel global-shutter mode with a -180dB PLS and 2Mpixel 10,000fps high speed image capturing are achieved.
A 3D stacked CMOS Image Sensor with a low noise technique:
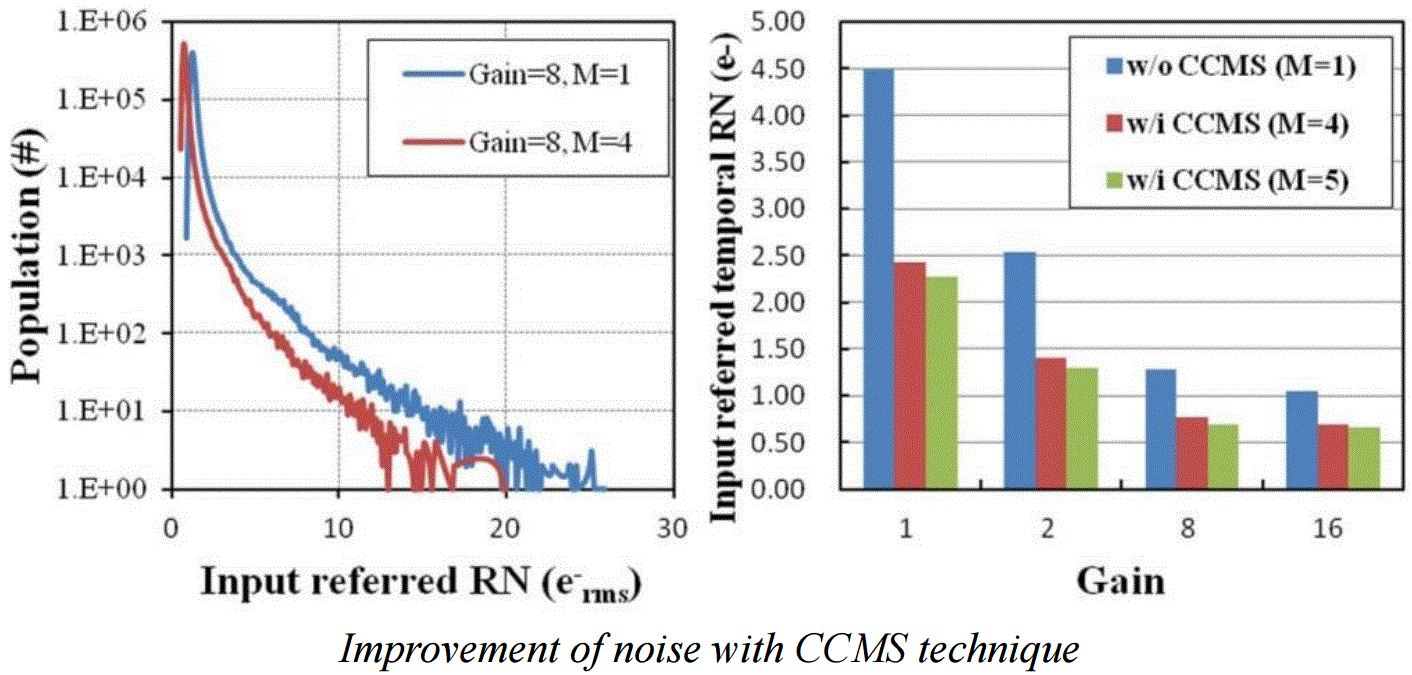
The paper by Shang-Fu Yeh, et al., of TSMC will describe an 8Mpixel 3D-stacked low noise CMOS image sensor with Conditional Correlated Multiple Sampling (CCMS) technique. This technique is proposed to solve the low frame rate issue by using multiple small-range voltage ramps. A 0.66e-rms input referred temporal readout noise is obtained with a 5-times CCMS technique, and also both thermal noise and the random telegraph signal (RTS) noise can be
reduced by using CCMS technique.
A 3D stacked CMOS Image Sensor with Global-shutter mode and high speed capturing mode:
The paper by Toru Kondo et al. from Olympus Corp. will describe a 16MP 3D stacked CMOS image sensor with pixel level interconnections using 4 million micro bumps. The two semiconductor substrates are bonded by a 7.6um pitch micro-bump array, and the storage node array is comprised on the bottom substrate to improve parasitic light sensitivity (PLS). Both a 16Mpixel global-shutter mode with a -180dB PLS and 2Mpixel 10,000fps high speed image capturing are achieved.
A 3D stacked CMOS Image Sensor with a low noise technique:
The paper by Shang-Fu Yeh, et al., of TSMC will describe an 8Mpixel 3D-stacked low noise CMOS image sensor with Conditional Correlated Multiple Sampling (CCMS) technique. This technique is proposed to solve the low frame rate issue by using multiple small-range voltage ramps. A 0.66e-rms input referred temporal readout noise is obtained with a 5-times CCMS technique, and also both thermal noise and the random telegraph signal (RTS) noise can be
reduced by using CCMS technique.