Bearing Systems
The first type of bearing system used with roller cone bits was a nonsealed,
roller-ball-friction bearing arrangement, utilizing rollers on the heel
of the journal. The primary load, or stress was exerted on these rollers, and
drilling fluid was used to lubricate the bearings. Bearing size was
maximized, since room for a seal was not required. The bearing surfaces
were machined and ground to very close tolerances to ensure dependable
service. This type of bearing system is also available with modifications for
air circulation and for use with a percussion hammer (Figure 3-6a).
The next generation of bearing systems was a sealed roller bearing system,
having a sealed grease reservoir to lubricate the bearings. The bearing
system is composed of: 1) a roller-ball-friction or roller-ball-roller bearings
2) the seal, which retains the lubricant and prevents drilling fluid and
abrasive cuttings from entering the bearing cavities, 3) the shirttail is
designed and hardfaced to protect the seal, 4) a lubricant, an
elasto-hydrodynamic type, is used to ensure minimum friction and wear, 5)
the reservoir, which stores and supplies the lubricant to the bearings, and 6)
the vented breather plug, which transfers downhole fluid pressure against
the lubricant-filled flexible diaphragm to equalize pressures surrounding
the bearing seal (Figure 3-6b).
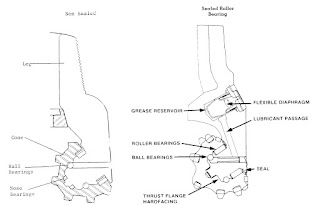
Figure 3-6a Figure 3-6b
There is, however, one serious drawback to the roller-ball-roller bearing
system. The primary cause of roller bearing failure is journal spalling,
which causes destruction of the rollers and the locking of the cone.
To remedy this, instead of the standard roller bearing assembly, the
“journal bearing” system utilizes solid metal bushings for direct cone to
journal contact. This offers a distinct mechanical advantage over roller
arrangements in that it presents a larger contact area at the load bearing
point. This distribution of the load eliminated the chief cause of roller
bearing assembly failure - spalling in the load portion of the bearing face.
Journal bearing systems in the tungsten carbide insert bits features a metal
bearing surface combined with a hardfaced journal and a lubricant.
Specialized seals and reliable pressure equalization systems keeps the
drilling fluid and formation contaminants out of bearings, and positively
seals the graphite-based lubricant inside the bearing. Precision fit of the
journal and cone distributes contact loading evenly throughout a nearperfect
arc. Bearing surfaces are finished to a carefully controlled surface
texture to ensure optimum lubrication.
The manufacturing of the journal bearing system consists of having the
journals either milled, grooved or pressed (depending on the bit company)
to accommodate the bushing. Then the bushings are inlaid on the journal.
Once the cone is fitted with teeth and gauge protection, the journal is then machine-pressed into the cone. To complete the seal between the cone and
the journal, special rings (seals) have been developed.
SealsThe first and still most popular seal is the radial seal (used mainly on the
sealed roller bearing bits). The radial seal is a circular steel spring encased
in rubber, which seals against the face of the shank and the face of the
cone. The newer “O” ring seal is considered the most effective seal. The
major problem confronting the “O” ring is tolerance, which must be precise
in order to maintain an effective seal.
An understanding of lubricants and lubricating systems is necessary for
successful drilling operations. The lubricating systems are essentially the
same, and are composed of an external equalizer located under the bit or on
back of the shanks, a grease reservoir with some sort of expandable
diaphragm to distribute the grease, and some sort of distribution system to
the bearings. In addition, there is a pressure relief valve to release any
trapped pressure, which might otherwise rupture the seals.
Pressure surges can be detrimental to these sealed systems. As pressure and
temperature increase, the viscosity of the lubricant increases. As a result,
the system cannot instantaneously compensate for abrupt changes in
pressure due to surges (going into the hole, making connections, etc.) and
small quantities of mud invade the system. With the close tolerance
necessary for effective sealing, mud solids can be damaging.
Adequate cleaning is even more important with sealed bearing bits. If
drilled cuttings are allowed to build up around the shirttail, seal damage
and premature bearing failure may result. Gauge protection is also
important to seal and bearing life, because seal damage can occur from
shirttail wear caused by inadequate gauge protection.
Any time a sealed bearing bit is rerun, the seals and shirttail should be
carefully checked for excessive wear or grooving.
To complete the journal-cone assembly, a positive seal is required to keep
drilling fluid out, while allowing the graphite lubricant in, which keeps the
bearings from overheating. The positive seal requires a relief valve to allow
escape of excess pressure, which can overload the seal and cause seal
failure.