Natural gas can occur by itself or in conjunction with liquid crude oils . It consists mainly
of the more volatile members of the paraffin series containing from one to four carbon
atoms per molecule. In addition, natural gases may contain varying amounts of carbon
dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide, helium and water vapour. Most natural gases
consist predominantly of methane, the percentage of which may be as high as 98 percent.
Natural gas can be classified as sweet and sour and as wet or dry. A sour gas is one that
contains appreciable amounts of hydrogen sulphide or carbon dioxide, and consequently
can be quite corrosive.
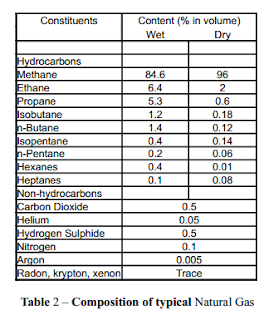
The designation wet gas has nothing to do with the presence of water vapour but signifies
that the gas will yield appreciable quantities of liquid hydrocarbons with proper
treatment.
Water vapour is, however, often present in natural gas and sometimes causes stoppages in
high pressure gas lines during cold weather. This is due to the fact that hydrocarbons
form solid hydrates with water at high pressure and low temperature.
Typical Compositions of wet and dry natural gas:Classification of natural gas based on Condensate/Gas Ratio:
Gas/condensate : gas/condensate ratio greater than 5 stb/million scf
Dry gas: gas/condensate ratio less than 5 stb/million scf




